Welcome! Here I’ll explain all the basics you need to know about the different types of loudspeaker systems, speaker components, and much more – along with examples of each.
Contents
What are the 4 main types of speakers today?
Getting good sound is still mostly the same as it has been for years and years but with a few changes to make enjoying music or movies even more convenient. Some of the best changes, in fact, are the type of speakers you can buy and use.
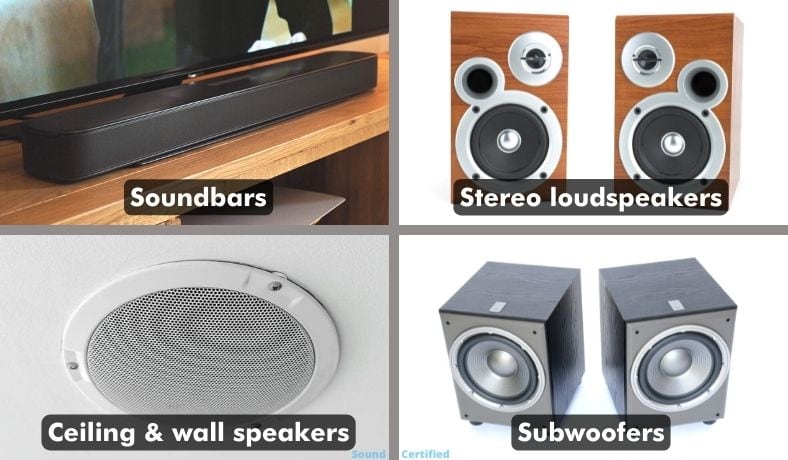
The most popular speakers used for home stereo systems are stereo loudspeakers, TV soundbars, ceiling or wall speakers, and powered subwoofers.
What are the most common car audio speakers?
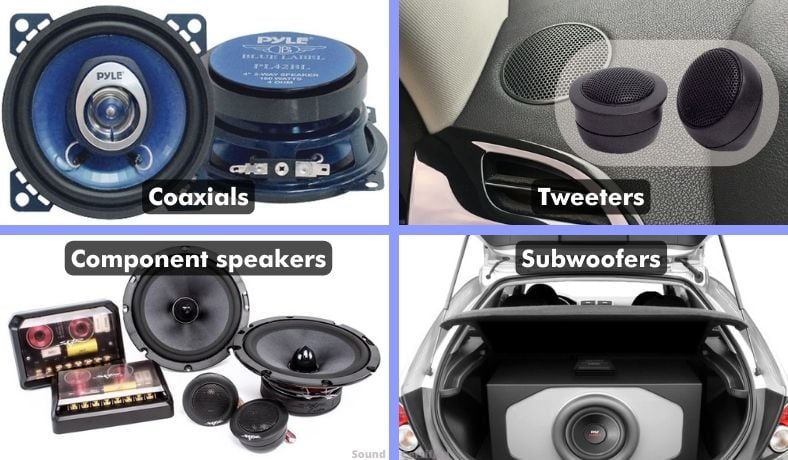
The most common vehicle audio speakers sold and installed today are coaxial speakers, component speakers (a type of 2-way or 3-way speaker system), tweeters sold in pairs, and subwoofers.
Factory-installed car speakers are typically single-cone speakers with an additional tweeter connected or a multi-speaker system with a component speaker design. These more advanced systems are typically present in premium-level options along with a factory-installed amplifier and even a compact subwoofer.
The different types of loudspeakers and speaker systems
Stereo loudspeakers
Standard 2-way and 3-way loudspeakers use 2 or more individual speaker units along with passive components to create high-quality full range sound. They’re typically sold and used as stereo speaker pairs, although additional pairs can be used for more sound and volume.
Stereo speaker systems, in most cases, need to be powered by a home stereo audio video receiver (AV receiver) or an audio amplifier.
Stereo 2-way and 3-way speakers
2 and 3-way loudspeakers are simply those that use multiple speaker drivers to produce high-quality sound, covering the full audio frequency spectrum. Hands down, they’re one of the most popular designs in the world as even budget models may have good sound quality.
A basic stereo speaker pair can recreate the left, right, and center placement of instruments, singers, and other sounds recorded in a studio.
- 2-way speakers use a tweeter and a woofer.
- 3-way speakers use a tweeter, a midrange speaker, and a woofer.
In both cases, the speakers use a passive speaker crossover to separate the audio signal. For example, the tweeter uses a high-pass crossover to play only bass (reducing distortion) and the woofer would receive only midrange and bass frequencies, blocking sound it’s poor at producing.
Bookshelf speakers
Bookshelf speakers are traditional stereo speakers that are small enough to fit on a bookshelf or even a desk. They typically use smaller woofers as well: 5 1/4″, 6″, and even 4″ or smaller in size.
Despite their small size, they’re capable of great sound with limited space. In fact, you can think of them as a scaled-down version of larger floor speakers.
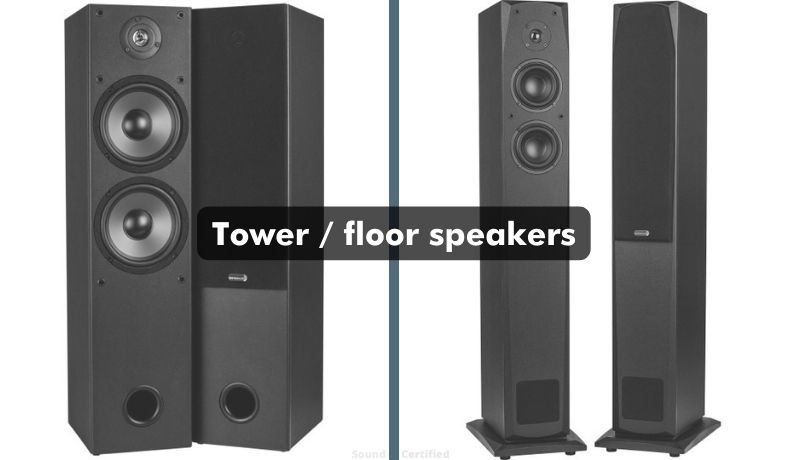
Tower speakers / floor speakers
Tower speakers are a type of floor speaker that uses a tall and slender design. Some designs also use multiple speaker drivers for enhanced sound production as they take advantage of the additional speaker enclosure volume available.
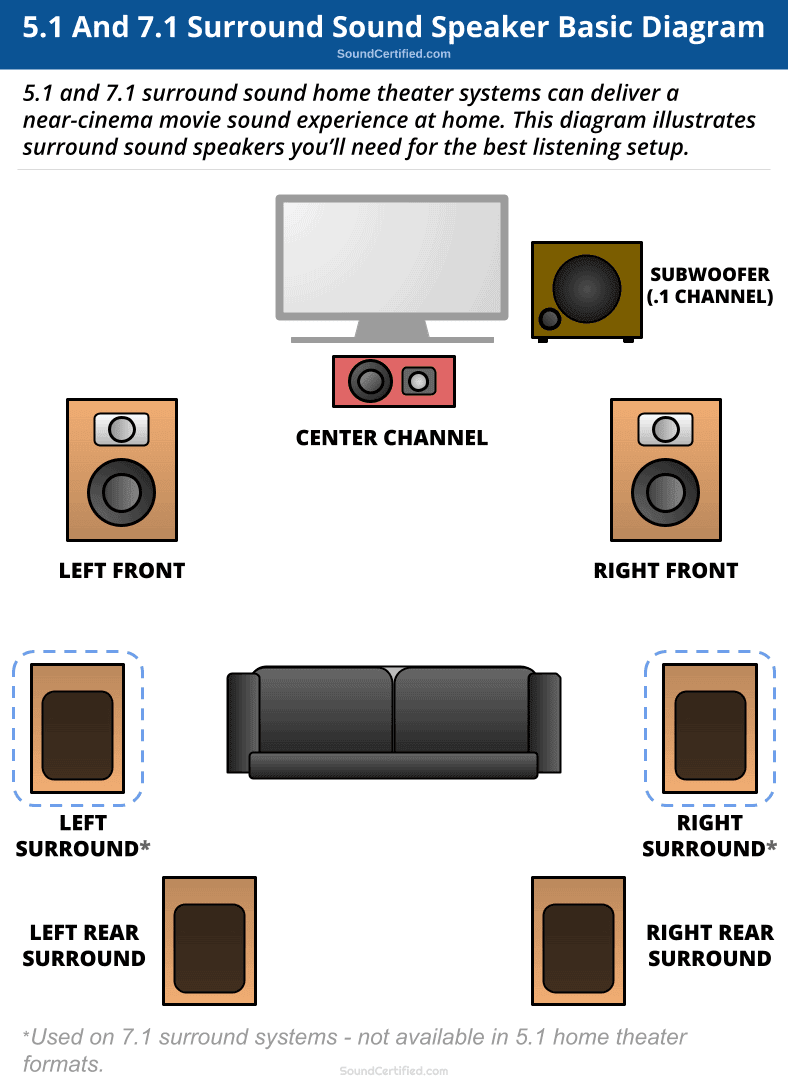
Surround sound speaker systems
A surround sound speaker system is the complete set of speakers needed to produce real surround sound playback from music and surround encoded music formats. This can be a 5.1 Dolby Digital or DTS encoded movie, for example, or a 7.1 channel type as more modern systems offer.
A true surround sound system uses the following speakers:
- Left and right front main speakers
- A center channel speaker.
- Left and right rear satellite speakers.
- A single mono subwoofer (usually powered)
The center channel signal can also often be sent to both the left and right front speakers, too, although you’re better off when possible using all the speakers supported by the format. For 5.1 digital sound, that’s 6 speakers total, and for a 7.1 system, that’s 8 in total (2 additional surround speakers).
Satellite / surround sound speakers
Satellite speakers are smaller units used to produce additional sound effects contained in movies and played back from a home theater setup. Many use a simpler design, even having a single cone driver (no tweeter), because of the limited audio range produced by surround sound encoding.
A satellite speaker pair is best used when properly located in a room so the effects can be heard as intended and mixed during movie production.
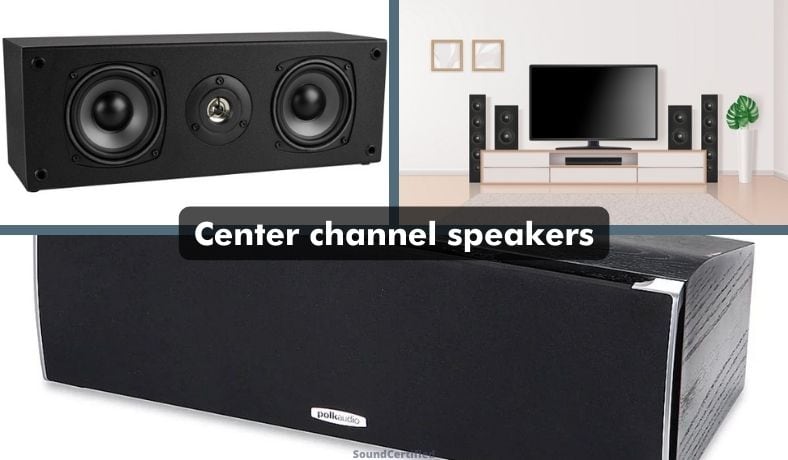
Center channel speakers
Center channel speakers are typically a compact speaker design used to produce vocals and midrange audio frequencies. Like satellite surround speakers, the center channel audio information in a movie is limited, and therefore, larger drivers aren’t required.
Better models, however, use a tweeter for enhanced speech production during playback.
Subwoofers
Subwoofers are optionally added to enhance the bass heard from music and movies because smaller speakers are poor at producing low frequency audio. Home audio and vehicle audio subwoofers come in two types:
- Non-powered (passive) models which require an amplifier channel and bass output from the source.
- Powered (active) models that are self-contained with an amplifier, low pass crossover, and matching enclosure.
Subwoofers are included with some home theater speaker systems as well as being sold separately. To correctly produce good audio, the speaker is matched to a properly designed bass enclosure that traps the sound waves and allows good bass response (good bass production).
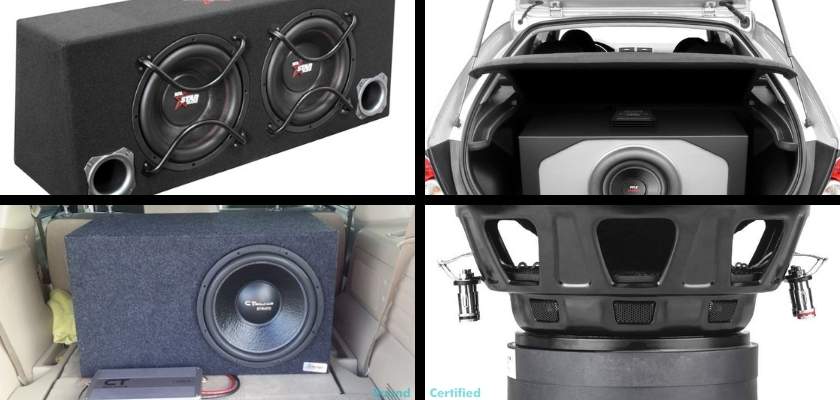
Car audio subwoofers
Car audio subwoofers are more or less the same a home theater and home stereo subwoofers, although they use different speaker impedance options such as 4 ohms, 2 ohms, and even 1 ohms. That’s due to the needs required to deliver large amounts of power in a vehicle unlike a home.
Car audio subwoofers also tend to have a very strong metal basket which is the speaker “frame.” They also often feature oversized magnets and voice coil wiring capable of handling hundreds of watts of power – if not even more!
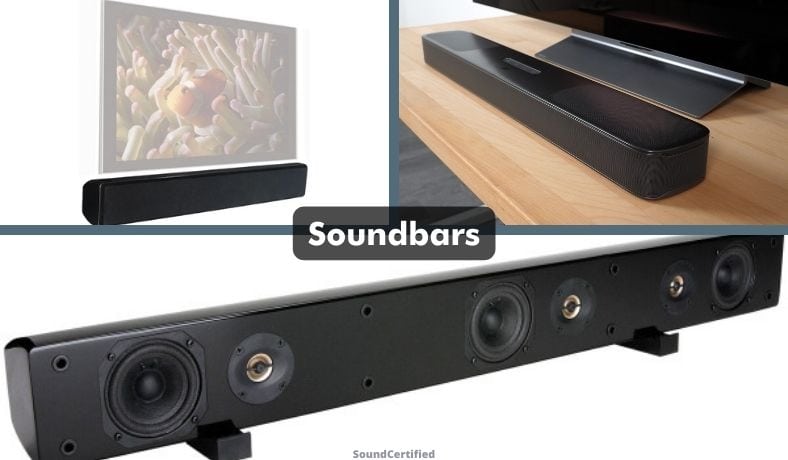
Soundbars
Soundbars are compact speakers that make it possible to improve your listening experience from a TV, cable receiver, or other media device with less space. They’re also more affordable than a complete speaker system.
Most soundbars are a type of powered speaker and contain a built-in power amplifier along with additional electronics related to audio signal compatibility.
They offer a variety of ways to connect to your television or other entertainment device depending on the particular model:
- Bluetooth or other wireless connectivity
- Standard stereo 3.5mm or RCA connections
- HDMI
- Using a digital audio connection (TOSLINK or coaxial digital inputs)
They’re especially great for people who don’t own their own residence as they can be moved relatively easily. However, a soundbar does limit the sound fidelity you can enjoy so they’re not without tradeoffs.
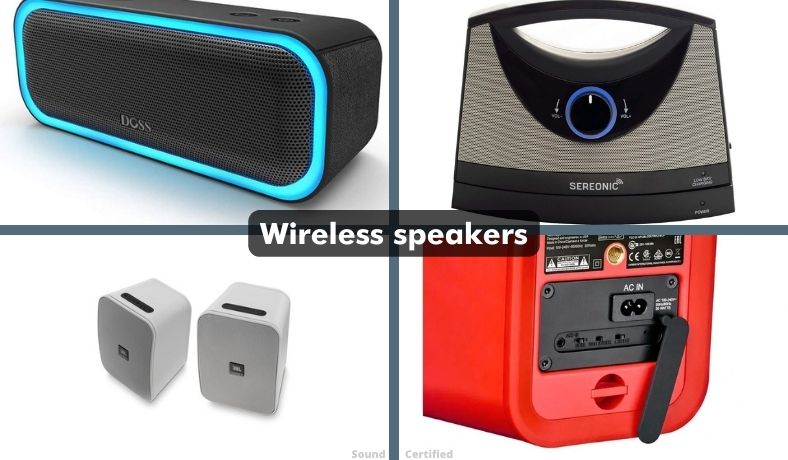
Bluetooth / wireless speakers
Wireless speakers make it possible to use speakers in inconvenient locations, where running or installing cables would be costly or difficult, and are easy to move from place to place.
They use audio that’s encoded, transmitted via a wireless signal protocol, received and decoded, and then amplification of the audio signal drives speakers.
Wireless speakers use one of several methods to transmit and receive audio:
- Bluetooth connectivity (digital)
- Over a Wifi network (digital)
- Analog encoded proprietary wireless signals.
A wireless speaker can even use a rechargeable battery for portability in many cases, although they do require a power source for charging or constant use. A Bluetooth speaker is excellent for portability and many are also water resistant.
Shower and bath speakers
Shower speakers/bath speakers are highly moisture resistant and also make listening to music in the shower or tub simple. Many are not stereo but mix both stereo channels into a combined monaural signal as they may use a single speaker to fit in smaller spaces.
Shower speakers sometimes feature a unique design allowing them to be hung from a water spigot, pipe, or bathroom items to avoid dropping them. These days, however, Bluetooth speakers sometimes make them a bit obsolete as they now offer similar features but with better sound production.
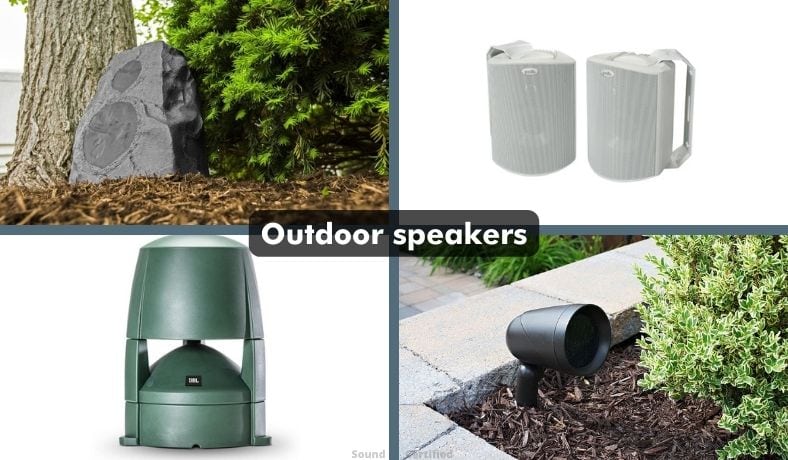
Outdoor speakers
Outdoor speakers are specially designed types that are resistant to outdoor environmental conditions and may even be designed to blend in with the environment. Outdoor speakers are typically powered by a standard home receiver or stereo amplifier in your house but can also be wireless.
Many use carbon fiber or plastic cone material that’s resistant to moisture unlike paper materials.
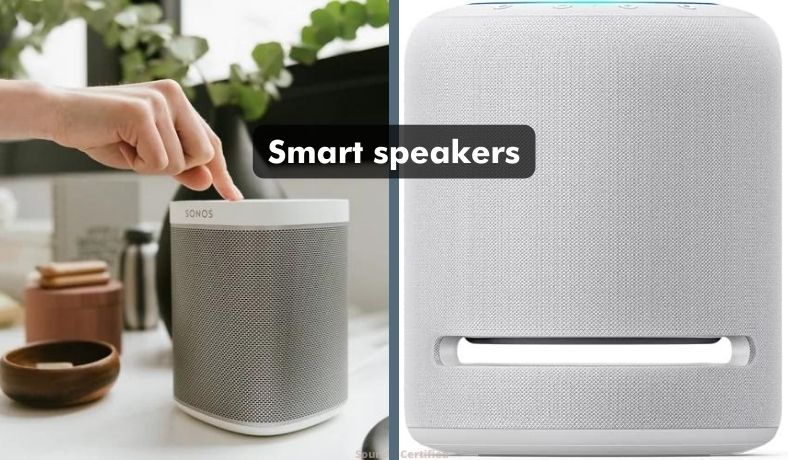
Smart speakers
“Smart” speakers are very unique in that they’re more of an entertainment device than simply a speaker in many cases, although they do share many similarities between brands and models. For example:
- A Sonos speaker works over Wifi to connect multiple speakers throughout your home. They, like others, allow you to stream music or other audio sources from your computer, smartphone, and online channels.
- Another example is the Amazon Echo line which are devices that work via Bluetooth and your internet connection. These provide voice commands for everything from setting reminders to music playback and even placing orders for what you need via the Alexa voice command system.
Smart speakers typically contain one or more speakers, an internal amplifier board, and sophisticated electronics for wireless connectivity and user feedback such as colored lighting or a display.
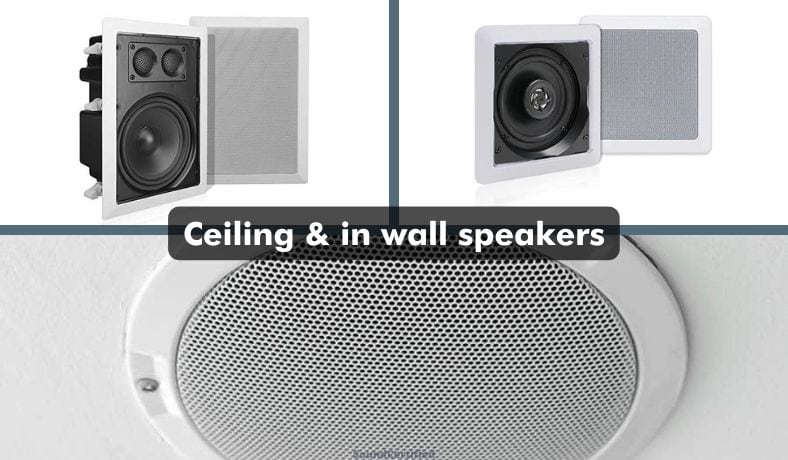
Ceiling speakers and in-wall speakers
Both in-wall and ceiling speakers offer some nice advantages: making good use of unused space and offering additional speaker locations, especially as surround sound systems. They’re also one of the best-looking options, too.
- In-wall speakers require cutting an opening in walls for flush mounting. They also require running speaker wire through walls and ceilings which is often best done during home construction.
- Standard home audio ceiling speakers have a 6 Ohm or 8 Ohm speaker impedance typically. They’re typically coaxial or 2-way speakers by design with full-range sound.
- Ceiling speakers used for commercial buildings or businesses often require a 70 volt transformer-based system which allows wiring many more speakers to the same audio amplifier. These normally have lesser audio performance and audio quality than home stereo ceiling speakers.
Although their installation can be a challenge, wall speakers are a great option if you’re after multiple satellite surround sound speakers similar to a real movie cinema experience.
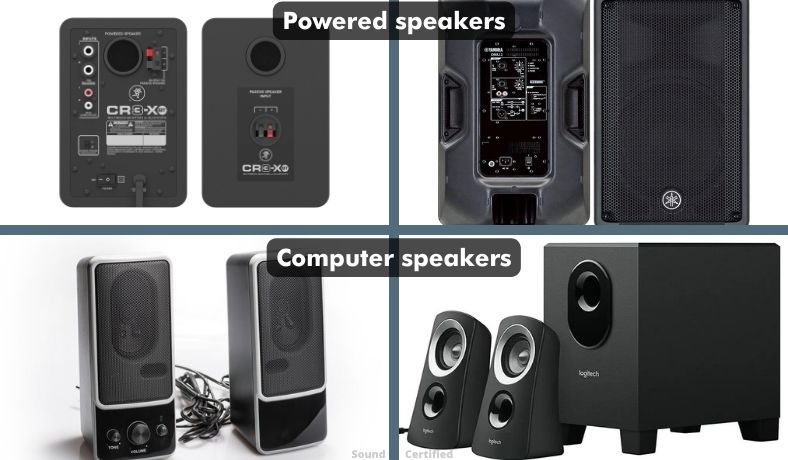
Powered speakers and computer speakers
Powered speakers are those which contain a miniature speaker amplifier system along with the electronics required to work with audio signals from a source. Powered speakers can also be a full multi-speaker system including a subwoofer all wired to a single amplifier board hidden inside one or more of them.
Because personal computers and laptops don’t provide an amplified speaker output feature, computer speakers make it easy to get sound without headphones or a wireless signal. Some can even be powered by a USB power source and are easy to use, although budget models tend to have poor sound as they use very inexpensive parts.
Speaker driver types
Individual speakers used to build a speaker system are sometimes referred to as speaker drivers. Here I’ll list the basic (and most common) types along with the frequency response (frequency output range) they’re capable of.
Tweeters
Tweeters are smaller speakers that produce high-frequency sound, often called treble. They’re responsible for the upper range of sound that gives music its crispness.
Tweeters typically use a very small cone because high-frequency sound waves have a smaller wavelength (smaller size) and don’t require a large cone. Tweeter speakers are used with a high pass crossover because they cannot produce bass and midrange frequencies.
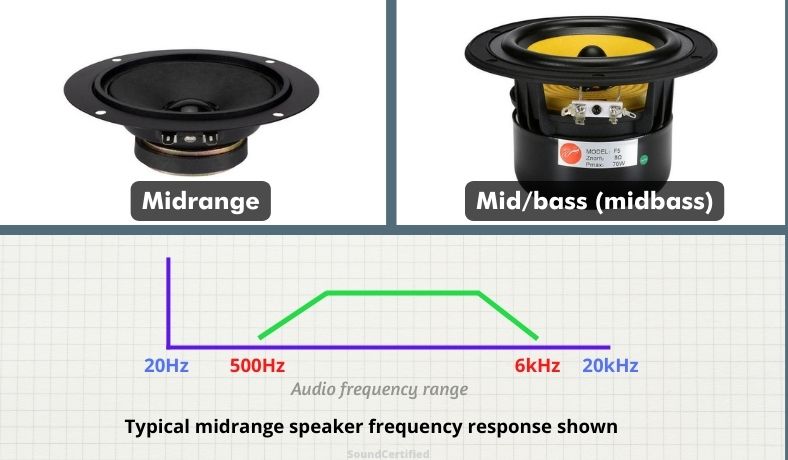
Midrange / midbass speakers
Midrange speakers are those that perform best for the midrange area of the sound frequency range. Some typical ranges they can produce are about 500 to 4 kiloHertz (kHz) but this varies by the particular speaker. Well-made designs can produce very detailed midrange sound.
Midbass speakers are those that produce midrange sound but also lower frequencies down to part of the bass region. They’re typically used with woofers or subwoofers as well. For example, you might a expect a midbass driver to be capable of bass down to 120Hz or even lower.
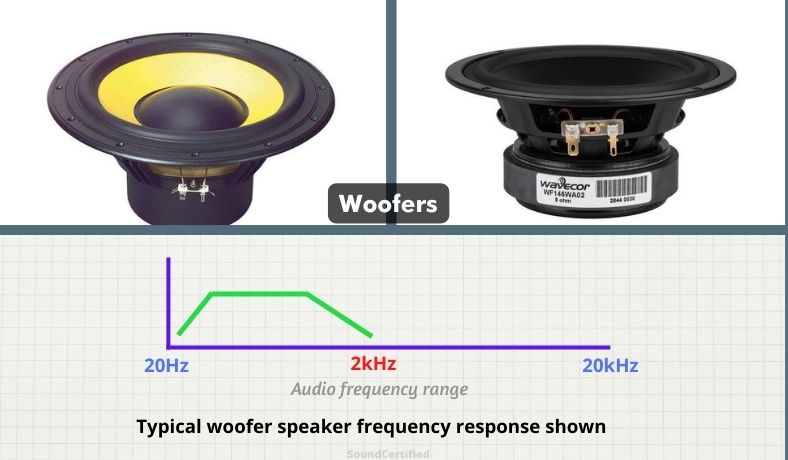
Woofers
Woofers and midbass drivers are sometimes extremely similar in what they do and at times have their names used interchangeably. However, generally, speaker woofers are speakers that can produce lower bass and midrange frequencies up to a range where a tweeter takes over.
For that reason they’re extremely common in 2-way speaker designs. Woofers do produce bass, although generally they can’t produce it at levels subwoofers can.
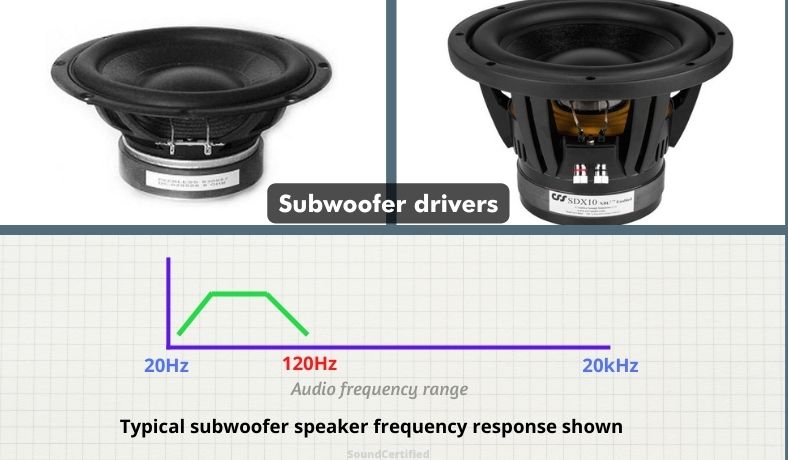
Subwoofers
A subwoofer driver is a type of speaker that’s only ideal for very low bass frequencies – from about 30Hz to 120Hz (or a bit more), for example. Subwoofers generally have a very large speaker cone made of a very heavy, durable material along with a very large magnet assembly and high power voice coil.
Subwoofers vary in power handling but generally can handle very large amounts of continuous power in addition to having a suspension & cone that can handle more extreme movement. Subwoofers use either a sealed speaker enclosure or a ported enclosure for additional low-frequency performance.
Passive subwoofers are simply those without an amplifier provide inside the speaker enclosure while active models have an amplifier built-in. They also feature a low-pass crossover for clean bass sound.